TREATMENTS
What is the retina?
Retina is an inner layer formed by nerve fibres and supporting tissue which help us in getting the sensation of light. It transmits the images to the Brain.
What happens to the retina in Diabetes
If the blood vessles which supply oxygen and nutrients to this layer are affected by Diabetes, these blood vessles become weak and start leaking blood and protein rich fluid in the supporting tissue. This results into deficiency of oxygen required by the retinal layer and to compensate for it, new blood vessles tend to grow in this area. These new vessles are fragile and they bleed and produce scar tissue, which can lead to permanent blindness.
When do these changes appear?
These changes usually are very slow in their occurence.and are helped by high or fluctuating blood sugar and high blood pressure. Though these changes can not be perceived by the patient in the early and treatable stages, your eye doctor can detect them during your retina examination
Do all diabetics develop retinal problems?
NO! Not all the patients with diabetes have vision problems. Good sugar control especially in the first 5 years after the detection of diabetes renders some protection against retinopathy changes. Associated high BP, Cholesterol, Anaemia, Kidney Problems can worsen eye problems. The discipline and control may result into long term benefit of reduced complications.
What will your doctor do?
A thorough eye examination is mandatory. Your doctor will examine your retina and grade it according to an International Classification which is the standard of practice everywhere in the world. Whenever required you will need to undergo a Fundus photography which helps document the stage of your eye and will also help compare the status at your next visit. An Optical Coherence Tomography is done when there is suspicion of swelling at the macula. This is like a virtual view through a microscope and shows the various layers in the retina. A Fundus Fluorescein Angiography is done when indicated. This helps us identify the areas at fault and direct our treatment strategy accordingly. It uses a Fluorscein dye which leaks through damaged and new blood vessles and gives useful information. Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation) : Laser is a powerful tool to reduce complications and maintain useful vision. it uses a focused beam of light and is used in the management of macular edema and new vessel formation in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Vitrectomy Surgery : Some patients may experience bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage), which makes it impossible for the laser to be delivered to the back of the eye. In most cases, vitreous hemorrhage clears up on its own. However, if it does not clear up after six weeks, a vitrectomy may be necessary. A vitrectomy may also be needed if tractional retinal detachment occurs. In this case, the surgery is performed to stabilize vision and reduce the risk of vision getting worse. A vitrectomy is a commonly performed retinal surgery. During the surgery, vitreous gel is removed using tiny instruments. The surgery is performed in a hospital setting, but on an outpatient basis. If scar tissue has built up on the retina, tiny instruments are utilized to remove the scar tissue. Laser treatment is also typically done during surgery. During surgery, patients are in a semi-sleepy state. The eye is numbed. The surgery lasts about half an hour to three hours, depending on the complexity of the situation. A gas bubble is usually placed inside the eye to serve as an internal “splint” until the retina heals. Over the course of several weeks, the gas bubble is absorbed. In more complex situations Silicone Oil is used instead of the gas.
What is a cataract ?
Cataract is clouding of the eye's natural lens. The lens works much like a camera lens, focusing light onto the retina and the back of the eye. The lens also adjusts the eye's focus, letting us see things clearly both up close and far away. With age this naturally transparent lens undergoes changes in its proteins to become opaque.
How will I know if I have a cataract?
At first there is little effect on your vision. There may be some blurring as though you are looking through a glass or a cloud. The vision further lessens and affects your daily activities only when it reaches an advance stage.
Cataract Treatment
When symptoms begin to appear, you may be able to improve your vision for a while by using new glasses, strong bifocals, magnification, appropriate lighting or other visual aids. Think about surgery when your impaired vision affects your daily life. Since there is no proven medical treatment for cataract in the form of eye Dr.ops or medications or injections, cataract surgery continues to be the recommended way of treating an eye with cataract. Cataract surgery is usually done on a day care basis. It doesn’t involve a prolonged hospital stay or restricted post operative activity.
Will it be a complicated surgery?
Cataract surgery is one the safest and most commonly performed procedures in ophthalmology. Cataract surgery today is the result of extraordinary technological and surgical advancements that allows millions of people to once again enjoy crisp and clear vision. A true marvel of modern medicine, cataract surgery may restore vision to levels you may have never thought possible.
Walk me through the process…
The surgery done today is called the Phacoemulsification Surgery Upon arrival for surgery you will be given eye Dr.ops and perhaps medications to help you relax. A local anesthetic either as injection or Dr.ops will make the operation painless. Most cataract surgeries are now performed using microscopic 2-3mm sized incisions, advanced ultrasonic equipment to break the cataracts into tiny fragments, and foldable intraocular lenses (IOLs) to maintain small incision size. Surgery is usually completed in a short period. Patients are asked to remain still during the procedure and to inform the surgeon if needing to cough or otherwise move for any reason. Once the surgery is complete, the patient will be briefly monitored, post-operative instructions given, and in most cases, the patient may be discharged within an hour. Intra Ocular Lenses Various types of 10Ls are available for the patients choice. Benefits of small, microscopic incision is maintained by foldable I0Ls, which can be inserted through less than 3 mm incision in the eye. Skillful surgery by an experienced Phaco surgeon, Latest state of the art equipments, higher end Zeiss and Moller Wedel Microscope and Alcon Centurion Vision system AMO White star Phaco machine; with well equipped Air Conditioned operation theatre and Laminar flow and positive air pressure system are the special touches we have added to make your surgery safe and comfortable and allow you to go home in just a couple of hours.
Get ready to have a painless, Smooth and satisfying eye surgery experience!
Dr.ive away your fears by discussing the details with your eye surgeon.
Why is it important?
Childhood should be a beautiful journey and to help our children enjoy it to the fullest, we must ensure that they have healthy eyes. Moreover most children find to difficult to express their eye problems, and hence, parents play the pivotal role in getting their children’s eye check-up done every year.
What types of examinations do pediatric ophthalmologists perform?
Vision assessment- Particular skills are needed to test a child’s eyesight, especially in the pre-school children. Different methods are used for different ages.
Determination of refractive error (the need for and strength of glasses) - This testing is performed after dilation in most pediatric patients to ascertain an objective measurement.
Motility examinations- Quantitative measurements of ocular misalignment are necessary for planning medical and surgical management of squint.
Biomicroscopy and dilated fundus examinations- These are necessary to investigate for the presence of eye disease associated with systemic diseases such as diabetes, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, genetic abnormalities, neurologic pathology (increased intracranial pressure), as well as specific ocular conditions such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Examination under anesthesia (EUA) - This may be necessary to diagnose and/or treat conditions in patients who will not allow adequate examination/treatment in the office. Monitor diseases over time and determine if the treatment is working properly, and make appropriate modifications if it is not.
What kind of treatments may be required?
Medical treatments:
-Prescriptions for glasses and/or contact lenses.
-Amblyopia (“lazy eye”) therapy including glasses, patching and pharmacologic treatment.
-Topical and or/systemic therapy for eye infections, chalazia, glaucoma, blocked tear ducts, and inflammation on the eye or in the eye.
- Surgical Procedures:
-Probe and Irrigation for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (blocked tear duct). -Excision of chalazia.
-Eye muscle surgery for strabismus.
-Pediatric cataract extraction including use of intraocular lenses (IOLs).
NOTE: Not all practitioners perform all medical and surgical treatments. Variability is due to the training, experience, and interest of the individual pediatric ophthalmologist. Additional treatments/surgeries performed by some include retinal examination and laser treatment of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), surgical removal of pediatric orbital tumors/lesions, and surgery for glaucoma or ptosis (drooping eyelid) in the child.
Refractive eye surgery is any eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses.
This can include various methods of surgical methods of remodeling of the cornea or cataract surgery. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea.
Successful refractive eye surgery can reduce or cure common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism, as well as degenerative disorders like keratoconus.
Who can undergo refractive surgery?
Those above the age of 18-21 years with a stable spectacle power for the past 1 year are eligible for this procedure. Generally the option of refractive surgery is offered to those having a high glasses power, those with a refractive error involving only one eye and those who do not have any other eye problems like dry eyes, retinal problems, glaucoma etc.
How long will rest be required?
A rest period of about 1 week is sufficient post laser procedures. The patient can begin light routine work after about 1 week and will have to put the drops that the doctor has advised.
Are there any risks?
This is considered a safe surgery, albiet with a strict selection process to ensure safety. There are stringent rules to give a green signal for refractive surgery, and once the protocols are followed, the procedure is safe and is being done with commendable success worldwide.
Eye injuries are emerging as one of the most devasting causes of loss of vision in all age groups.
What are the common eye injuries?
Road traffic accidents, injuries during manual labour, injuries due to chemicals, Firecracker injuries in adults and children, and injuries in children while playing.
Can vision be preserved after all injuries?
The type and site of injury dictates the outcome. Immediate treatment and adequate post operative care can help prevent blindness in such cases.
Ocular trauma care is a challenging branch and not all centres are equipped with trained doctors, hospital personnel and instruments to handle such crises. At our centre, we ensure prompt attention to these delicate issues and provide meticulous treatments to all kinds of ocular emergencies. Our staff has been specially trained to identify the probable causes and problems and start the process of management of the trauma right away.
What can possibly be an emergency for an eye?
Trauma to the eye, Sudden loss of vision, redness or severe pain are all treated as ocular emergencies and hence warrant immediate attention. Blockage of retinal arteries, severe conjunctival or corneal infections, retinal detachments can all cause sudden drop in vision and hence distress to the person. These have to be recognized and dealt with at the earliest.
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a common eye condition in which vision is lost because of damage to the optic nerve. The optic nerve carries information about vision from the eye to the brain. In most cases, the optic nerve is damaged when the pressure of fluid inside the front part of the eye rises. However, glaucoma-related eye damage can occur even when the fluid pressure is normal.
- Who is at risk for glaucoma?
- Age above 40
- Family history of glaucoma
- High minus number
- Diabetes, hypertension or heart disease
- High intraocular pressure (IOP)
- Eye pain due to previous surgery
Although open angle glaucoma and closed angle glaucoma both can cause blindness, their symptoms are very different.
Open Angle Glaucoma — In this form of glaucoma, vision is lost painlessly and so gradually that most people do not realize they have a problem until substantial damage has occurred. Peripheral vision (at the edges) is usually lost first. As larger areas of your peripheral vision fade, you may develop tunnel vision — vision that has narrowed so you see only what is directly in front of you, like looking through a railroad tunnel. If glaucoma is not treated, even this narrowed vision disappears into blindness. Once gone, areas of lost vision cannot be restored.
Closed Angle Glaucoma — Symptoms of acute glaucoma occur suddenly and can include blurred vision, pain and redness in the eye, severe headache, halos around lights at night, a haziness in the cornea (the clear front portion of the eye in front of the pupil), nausea and vomiting, and extreme weakness.
Glaucoma is a lifelong illness, but proper treatment can prevent loss of vision.
What are the treatment options for glaucoma? Glaucoma is treated with a number of drops, in order to reduce pressure. Surgery is required in few cases.


Glasses can be a cause of distress for those who have to use them every day and are dependent on them! Newer advances in contact lens technology has improved the quality of vision and the comfort level of the lenses. We now have the luxury to be able to choose from a wide variety of options with respect to contact lens types. We will help you get the most of the lenses you choose and help you understand how to use them best. Soft Contact lenses, RGP lenses, Toric Contact lenses, Scleral lenses, Prosthetic lenses are the available options for management of various eye conditions. Right from simple refractive errors to keratoconus to severe dry eye conditions, numerous patients have obtained relief from their eye problems.


Vision is by far one of the most valuable and delicate privileges available to man. However when certain conditions like retinal diseases, congenital eye diseases and other corneal conditions cause a considerable loss of vision, any vision that can be added to the existing vision is an invaluable gift to the person. These low vision aids provide definite improvement in quality of life for individuals with Age Related Macular degeneration, Congenital Retinal illnesses like Retinitis Pigmentosa and other pigmentary dystrophies, corneal opacities and many such illnesses. The goal of low vision therapy is to increase the functionality and increase the patient’s ease in everyday activities. The available instruments are magnifying spectacles, hand and stand magnifiers, telescopes, CPF glasses, CCTVs, writing aids, smartphone assisted devices.

ALL WORK AND NO PLAY DOES MAKE JACK A DULL BOY!
The importance of playgrounds and games for children can never be more important than now! With increasing number of gadgets overpowering our daily routines, outdoor activities need to be given more precedence than they are getting now!
There is growing evidence from both human and animal studies of refractive error showing that ambient light exposure is an important environmental factor involved in the regulation of eye growth. Documented seasonal variations in eye growth and refractive error progression in childhood (with slower eye growth seen in summer months and faster rates of eye growth in winter months) support a potential role for ambient light exposure in the control of human eye growth.
Documented seasonal variations in eye growth and refractive error progression in childhood (with slower eye growth seen in summer months and faster rates of eye growth in winter months) support a potential role for ambient light exposure in the control of human eye growth.
Indian population : 13.1% school children have myopia. There is a positive association of myopia with studying in private schools vs. government schools, positive family history, higher socio-economic status, studying/reading > 5 hours per day, watching television > 2 hours / day and with playing computer/video/mobile games.
An inverse association with outdoor activities/playing is observed with children playing > 2 hours in a day. SO LET THE CHILDREN PLAY OUTSIDE. A LITTLE SUN AND TAN WILL DO NO HARM! North India Myopia Study (NIM) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342249/ Role of Outdoor Activity in Myopia (ROAM) Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4342249/






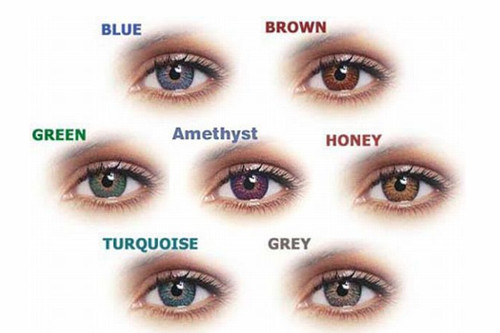
 Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
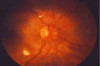
 Cataract Surgery
Cataract Surgery
 Pediatric ophthalmology – childhood eye diseases
Pediatric ophthalmology – childhood eye diseases
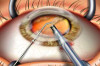
 Refractive surgery
Refractive surgery
 Ocular Trauma and Emergency Services
Ocular Trauma and Emergency Services
 Glaucoma Services
Glaucoma Services

